
DL-Dithiothreitol – DTT as key element in diagnostics
In today’s time when there is still no vaccine or medication against the corona virus, COVID 19 tests or antibody tests are particularly important in order to uncover and thus interrupt the chain of infection. One product is of particular importance in these test kits: DL-Dithiothreitol, in short: DTT
Long-term partnership
Cfm Oskar Tropitzsch GmbH is the exclusive partner of the Indian manufacturer Siddhi Vinayaka Spechem Pvt. Ltd. from Bangalore for DL- Dithiothreitol.
DTT according to customer’s needs
As standard we can offer you three different qualities: Standard Grade, Pure Grade or Biotech Grade. Of course, we can manufacture DTT according to your specification as well.
ARTICLE NUMBER: 3483-12-3
CAS NO.: 3483-12-3
FORMULA: C4H10O2S2
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 154,25 g/mol
ARTICLE NUMBER: 5250052
CAS NO.: 3483-12-3
FORMULA: C4H10O2S2
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 154,25 g/mol
ARTICLE NUMBER: 5250051
CAS NO.: 3483-12-3
FORMULA: C4H10O2S2
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 154,25 g/mol
Dithiothreitol is the trans isomer of the compound 2,3-dihydroxy-1,4-dithiolbutane. DTT, also known as Cleland’s Reagent, is a cell-permeable, strong but mild reducing agent, with a low redox potential of -0.33 V at pH 7 (optimal pH range 7.1 to 8.0). This allows it to reduce practically all accessible biological disulfides, as well as to protect free thiols from oxidation.
The reduction of disulfide-containing compounds by Dithiothreitol is a two-step reaction. First, DTT forms a mixed disulfide with the target molecule in a reversible reaction, reducing one sulfur to the corresponding sulfhydryl. In the second step, intramolecular cyclization of DTT leads to an energetically favored six-membered cyclic disulfide. This drives the reaction to completion, reducing the second sulfur of the original disulfide bond. Consequently, DTT is required in much lower concentrations compared to monothiol reducing agents (e.g. glutathione or 2-mercaptoethanol). The latter are usually required in extreme excess to completely reduce target compounds.
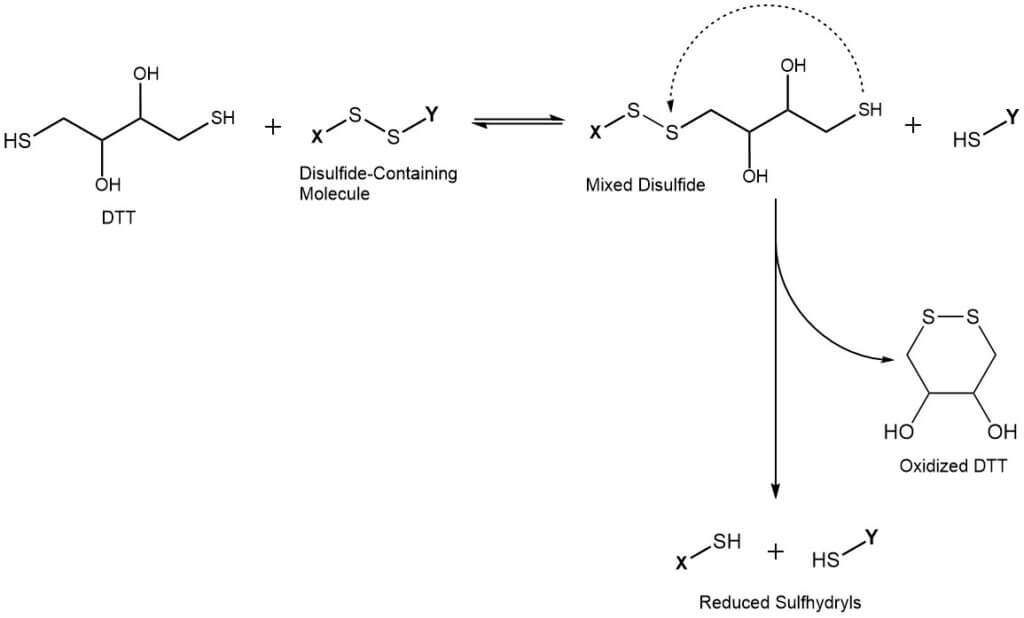
Applications of DTT
Most commonly, Dithiothreitol is used to reduce disulfide bonds in peptides and proteins. However, as with all reductants, DTT can only reduce disulfides if they are accessible. At low concentrations, DTT can be used to stabilize proteins with free thiol groups. Conversely, high concentrations of DTT are utilized in order to denature proteins, e.g. before performing an SDS-PAGE.
In recombinant protein expression, the formation of insoluble inclusion bodies is a frequently encountered problem. Dithiothreitol is an integral reagent, together with denaturants such as GdmCl, for the solubilization of proteins from inclusion bodies.
DTT is also employed for the cleavage of disulfide-containing crosslinkers or modifications. For example, two macromolecules connected by a disulfide-bearing crosslinker may be separated again if desired by mild reduction. This technique is frequently employed in the analysis of receptor-ligand interactions, as well as in the study of protein-protein interactions in vivo.
Due to its strong reduction potential, DTT can also be used to reduce organic azides to their corresponding amines in a pH range of 7.2 – 9.0. Common conditions for azide reduction include Staudinger conditions using phosphines, catalytic hydrogenation, and reduction by stannous chloride. In contrast to reduction by DTT, however, none of those methods are both mild and selective, while allowing for the complete removal of reactants after completion.




 4c media
4c media