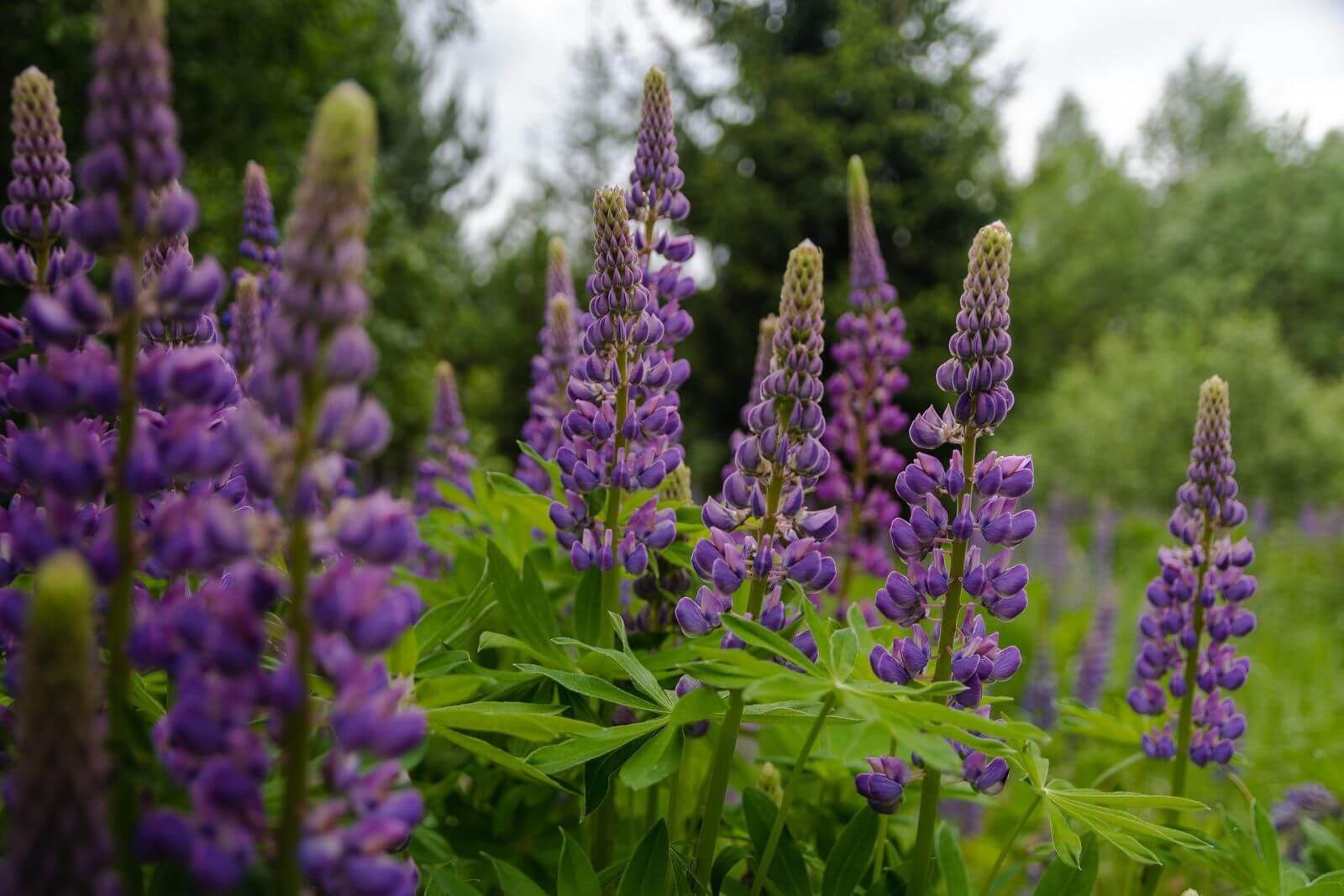

Lupins: vegetable protein source
Lupine seeds, which are particularly high in protein, have long been considered an alternative to soy. Slowly but surely, lupine products are conquering the food market – and not without reason.
Already in ancient Egypt, around 2000 BC, the lupine was considered one of the most important foods next to grain. Even then, people knew about the bitter and poorly digestible ingredients, the so-called alkaloids. To make them more tolerable, our ancestors washed the seeds in the sea. Fortunately, this is no longer necessary today, because low-alkaloid varieties are now being bred: the so-called sweet lupins.
Botanically, the lupine is a legume, similar to peas or beans. After the magnificent flowering, the pods on the stems are up to seven centimeters long and contain the seeds. These are harvested with the combine harvester.
Lupine Seeds: gluten-free flour, high-protein breads, and more
Lupine seeds cannot be bought in unprocessed form, as they contain residues of alkaloids and must first be tested. The gluten-free flour made from lupine seeds, on the other hand, can be found in any well-stocked health food store.
Protein-rich breads made from lupine meal are becoming increasingly popular because, in contrast to normal bread, they contain fewer carbohydrates and are therefore low-carb foods. Lupins are also an insider tip among vegans and vegetarians, because the soaked beans can be easily processed into a meat substitute.
The legume can even be found in some coffee substitutes.
Lupins contain phytoestrogens
The protein content of lupins is considerable and, at up to 40 percent, can even compete with that of soybeans. It contains all essential amino acids as well as vitamins A and B1 and minerals such as potassium, calcium, magnesium and iron.
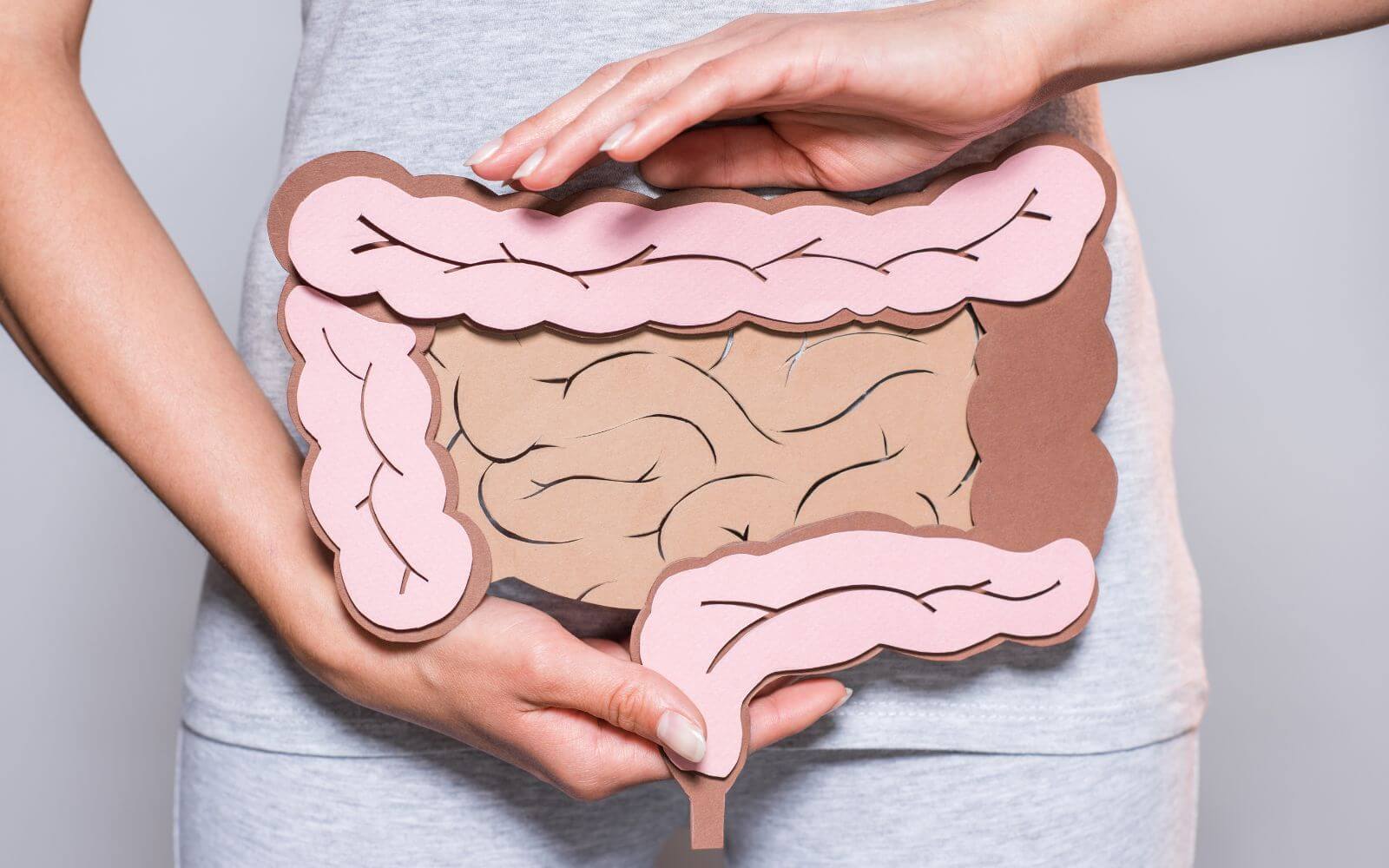
Similar to soybeans, phytoestrogens have also been detected in lupins. Phytoestrogens can protect against breast and prostate cancer, osteoporosis and cardiovascular diseases. In addition, the dietary fibers ensure faster intestinal transit, protect against colon cancer and can lower cholesterol levels.
With all health-promoting effects: People with a known peanut allergy should be careful! Peanut allergy sufferers can react violently to the consumption of lupine products.
Lupine plants improve the condition of the soil
Lupins are valuable not only for humans, but also for the soil. While soy is increasingly discredited in terms of rainforest deforestation and genetic engineering, lupins are gaining more and more attention. Lupine plants are considered frugal and robust. They defy great heat as well as frost. And even sandy soils are no obstacle for them to thrive. The nodule bacteria on the roots bind nitrogen and thereby improve the soil conditions. And with all the advantages, the plant does not need fertilizers.
We, Cfm Oskar Tropitzsch GmbH, offer the following quinolizidine alkaloids as reference substances:
- Albinhydrochlorid
- Anagyrin hyddrochlorid
- Angustifolin
- Cytisin
- 13-Hydroxylupanin
- Lupaninhydrochlorid
- Multiflorin
- Spartein




 4c media
4c media